Galvalume steel coil is a type of steel with a coating of aluminum and zinc, protecting it from oxidation. Learn more about the basics of galvalume steel coil.
What is Galvalume Steel Coil?
Galvalume steel coil is a type of steel coil that has a coating of aluminum-zinc alloy, which is applied to it through a continuous hot-dip process. The coating provides corrosion resistance to the steel. It is ideal for use in outdoor environments and in applications where moisture and humidity are present.
Galvalume steel coils are commonly used in roofing, siding, and other construction applications. They offer a combination of durability, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance that makes them a popular choice in extreme environmental conditions.
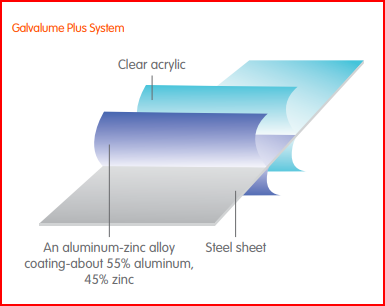
The name “Galvalume” is a combination of “galvanized” and “aluminum,” reflecting the fact that the coating is made up of both materials. The coating consists of aluminum (55%), silicone (1.6%), and zinc (43.4%).
The aluminum coating offers malleability, while the zinc offers galvanic protection for the steel from corrosion. This coating gives the steel a plain and smooth finish while ensuring long-lasting performance and aesthetic appeal for the finished project.
Galvalume Life Expectancy
Galvalume steel coils are resistant to corrosion and rusting, which means they can last for several decades even in harsh environments. According to research, galvalume has proven its outstanding performance in North America, which is prone to extreme conditions such as winter and acid rain.
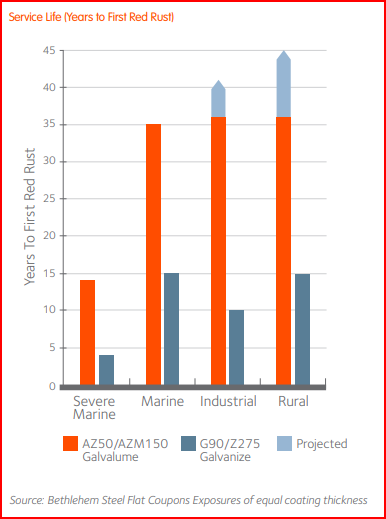
The outdoor exposure tests on actual building installations prove that Galvalume steel sheets and coils are more resilient and have better corrosion resistance than zinc-coated sheets with the same coating thickness under the same harsh conditions. The steel’s service life expectancy can reach an average of up to 35 years without regular maintenance.
Source: https://sadofascoprod.blob.core.windows.net/media/clhmvpyk/amd-0621-galvalume-brochure-update-en.pdf
The test also revealed that the service life of Galvalume could reach 40 to 60 years in both rural and industrial environments. The study consists of atmospheric tests in which researchers used flat coupon samples over a span of 17 years in Canada and over 36 years in the United States.
Superior Cut Edge Protection
Galvalume steel coils have superior cutting-edge protection due to their aluminum-zinc alloy coating. The coating on the steel substrate offers long-lasting protection against the elements that contribute to corrosion, especially on the exposed edges of the steel.
The protective zinc coating offers galvanic protection to the steel. It means that the zinc does not produce corrosion within the encapsulated steel. This technology extends the life of galvalume steel by preventing the degradation of the underlying metal over time.
The aluminum component of Galvalume offers a long-term barrier against corrosion. It gives protection to the exposed edges under harsh environmental conditions. The cutting-edge protection of Galvalume makes it advantageous compared to galvanized steel and aluminum-coated steel.
Although galvanized steel has less corrosion, it can produce red rust at the bare edges, while aluminized steel performs only in marine environments. Galvalume provides a longer-lasting barrier to degradation than other types of steel products.
Manufacture
Galvalume has an alloy coating of 55 percent aluminum, 43.5 percent zinc, and 1.5 percent silicon during the hot-dip process. Silicon acts as a barrier against the development of a breakable intermetallic layer. This layer develops during the hot-dip processing while the zinc coating takes place.
The molten coating and steel sheet interact during the manufacturing, affecting the coating’s adhesion during applications. The hard and brittle intermetallic alloy layer must remain thin during processing by adding silicon to the 55 percent aluminum-zinc bath. Silicon helps control the expansion of the alloy layer, making it formable during application.
Silicon does not have a role in preventing corrosion. Some applications of aluminum-zinc-silicon alloy-coated steel were not effective in deep drawing. Instead of using steel coils or sheets with a 55 percent aluminum-zinc-silicon alloy, customers prefer galvanized sheets.
Recent coating technology uses clear resin coatings known as 55 percent Al-Zn Plus, which are effective in some applications of deep drawing.
Source: https://sadofascoprod.blob.core.windows.net/media/clhmvpyk/amd-0621-galvalume-brochure-update-en.pdf
Coating Microstructure
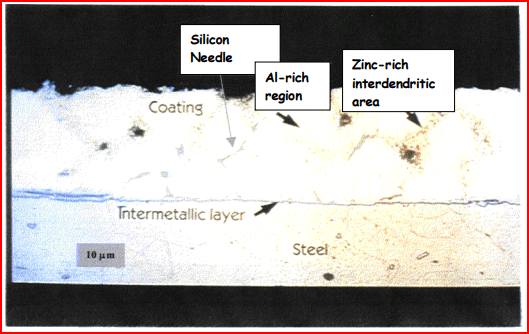
The 55% Al-Zn coating microstructure of galvalume consists of two phases. The first phase is known as the aluminum-rich dendritic phase, which develops during the solidification process. At this phase, the dendrite growth is due to the swift movement of the solid or liquid interface in the direction of the undercooled melt.
The second phase is known as the interdendritic zinc-rich region. It develops when the solidifying liquid’s zinc concentration is at its highest peak. The microstructure phases are vital to reaching the ideal corrosion resistance.
Apart from the two primary microstructural phases, there are other phases involved in the process, such as the intermetallic layer at the steel-coating interface and the discrete needles of the elemental silicon.
Note: See the figure below to find the interdendritic zinc-rich, aluminum-rich region, and the silicon needle. The figure describes the microstructure of a 55 percent aluminum-zinc coating.
Source: https://www.galvinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/8/2017/05/GalvInfoNote_1_4.pdf
Corrosion Resistance
Galvalume steel coils have superior performance compared to galvanized coatings in rural, industrial, and marine environments. The aluminum-zinc alloy coating has a unique dendritic structure that protects the steel from corrosion.
The zinc-rich areas are the first to corrode under harsh conditions. The corrosion rate decreases in the interdendritic areas of the coating because the corrosive products penetrate the interdendritic interstices. This development results in the flattening of the corrosion rate curve in various environments.
The 55 percent aluminum zinc coating corrosion behavior works differently with a galvanized coating, which has a uniform thinning process. The aluminum-rich dendrites act as a protective coating, while the zinc-rich regions offer galvanic protection to prevent rusting on the sheared and exposed parts of the steel.
Standard
Galvalume steel coil is manufactured according to different standards. It depends on the country or region where it is produced and used. Here are some examples of standards that are commonly used for galvalume steel coil:
- ASTM A792: This is the standard specification for steel sheets coated with a 55% aluminum-zinc alloy by the hot-dip process. This standard covers galvalume steel coil for use in architectural, building, and construction applications.
- JIS G 3321: This is the Japanese Industrial Standard for hot-dip, 55% aluminum-zinc alloy-coated steel sheet and strip. It covers galvalume steel coil for use in industrial and civil engineering applications.
- EN 10346: This standard refers to the European standard for hot-dip coated steel flat products for cold forming. This standard covers galvalume steel coils and sheets for use in construction applications.
- AS 1397: This is the Australian standard for steel sheet and strip, hot-dipped zinc-coated or aluminum zinc-coated. It covers galvalume steel coil and sheet for use in building and construction applications.
These standards specify the requirements for the different characteristics of galvalume steel coils. It includes the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, and surface quality of the products. The international standard-setting bodies ensure that the galvalume steel coil produced in different countries meets certain quality and performance standards.
Galvalume Steel Coil Process
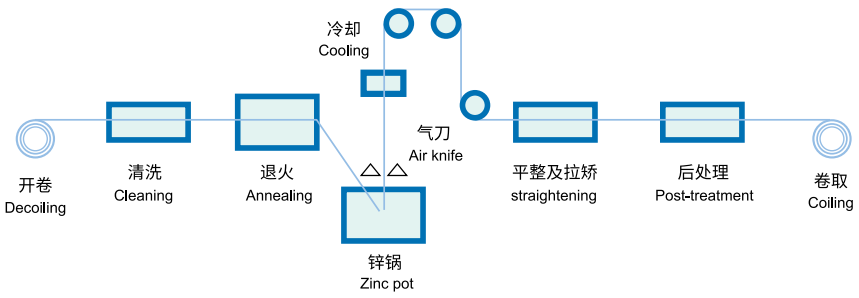
Decoiling – Cleaning – Annealing – Zinc pot – Cooling – Air knife – Straightening – Post-treatment – Coiling
Detailed steps of the galvalume steel sheet processing
Step 1:
Pre-treatment: After the cold-rolled coil arrives in the galvalume workshop, after passing through the uncoiler, through the degreasing section, and the reduction furnace, the steel coil is cleaned and its components are reduced to the extent that it can be galvanized.
Step 2:
Central section: The most critical technology is this step. After passing through the zinc pot, a layer of zinc layer is plated on the surface of the steel plate. After coming out of the zinc pot, it is cooled and shaped by the cooling tower.
Step 3:
Post-processing: The steel plate finally comes to the post-processing stage after various processes. After finishing, straightening and passivation, and finally coiling
Conclusion
Galvalume steel coil offers better corrosion resistance and formability than galvanized steel coil. The choice between the two depends on the specific application and the required performance characteristics.